What Is a Glioma? Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Gliomas are among the most common and complex brain tumors — but don’t worry. Depending on the type and grade, this stubborn disease can often be treated or controlled. Keep reading.
Gliomas are among the most common and complex brain tumors. This article explains what gliomas are, how they are diagnosed, and the advanced treatment options available in Istanbul.
A common question is: “What is a glioma?”
A glioma is a type of tumor that originates from glial cells within the brain or spinal cord. These are primary brain tumors, meaning they start in the central nervous system rather than spreading from elsewhere in the body. A glioma arises from the supportive tissue of the brain and can range from slow-growing to highly aggressive.
Glial cells play essential roles in maintaining and protecting neurons, as well as supporting electrical signaling. Genetic mutations in these cells can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation. Gliomas can affect both children and adults.
Types of Gliomas
Astrocytomas
Astrocytomas develop from star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes. They vary in behavior and are graded by the World Health Organization (WHO) from I to IV:
- Grade I (Pilocytic Astrocytoma): Typically found in children. These tumors grow slowly and can often be cured with surgery.
- Grade II (Diffuse Astrocytoma): Slow-growing but infiltrative, making complete surgical removal challenging.
- Grade III (Anaplastic Astrocytoma): More aggressive, with increased cellular activity and mitosis.
- Grade IV (Glioblastoma Multiforme – GBM): The most aggressive and deadly form, requiring a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Glioblastoma (GBM)
Glioblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in adults. It usually appears in the cerebral hemispheres and spreads quickly into surrounding brain tissue. It is often diagnosed at an advanced stage. Glioblastomas are known for their rapid growth and high invasiveness. They frequently present with headaches, seizures, or changes in consciousness. Standard treatment includes surgery followed by chemoradiotherapy.
Oligodendrogliomas
Oligodendrogliomas arise from oligodendrocytes — glial cells that produce the myelin sheath around nerve fibers. These tumors tend to grow more slowly than astrocytomas and often respond well to treatment. They are more common in adults and typically occur in the cerebral hemispheres. A key characteristic of oligodendrogliomas is the presence of a specific genetic signature: 1p/19q codeletion. This molecular marker helps guide treatment decisions and is associated with a more favorable prognosis compared to other high-grade gliomas.
What Are the Symptoms of a Glioma?
Glioma symptoms vary depending on the tumor’s location, size, and pressure on surrounding tissues. Common signs include:
- Morning headaches, sometimes with nausea or vomiting
- New-onset seizures
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech (aphasia)
- Visual disturbances such as blurred or double vision
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body (hemiparesis)
- Gait disturbances and balance problems
- Memory loss, confusion, or personality changes
Low-grade gliomas often produce subtle symptoms over time, whereas high-grade gliomas like glioblastoma may present acutely and progress rapidly.
How Is a Glioma Diagnosed?
Glioma diagnosis is managed by a multidisciplinary team using state-of-the-art imaging and pathology techniques.
Neurological Examination
A thorough clinical assessment evaluates motor function, speech, reflexes, coordination, and cognitive status.
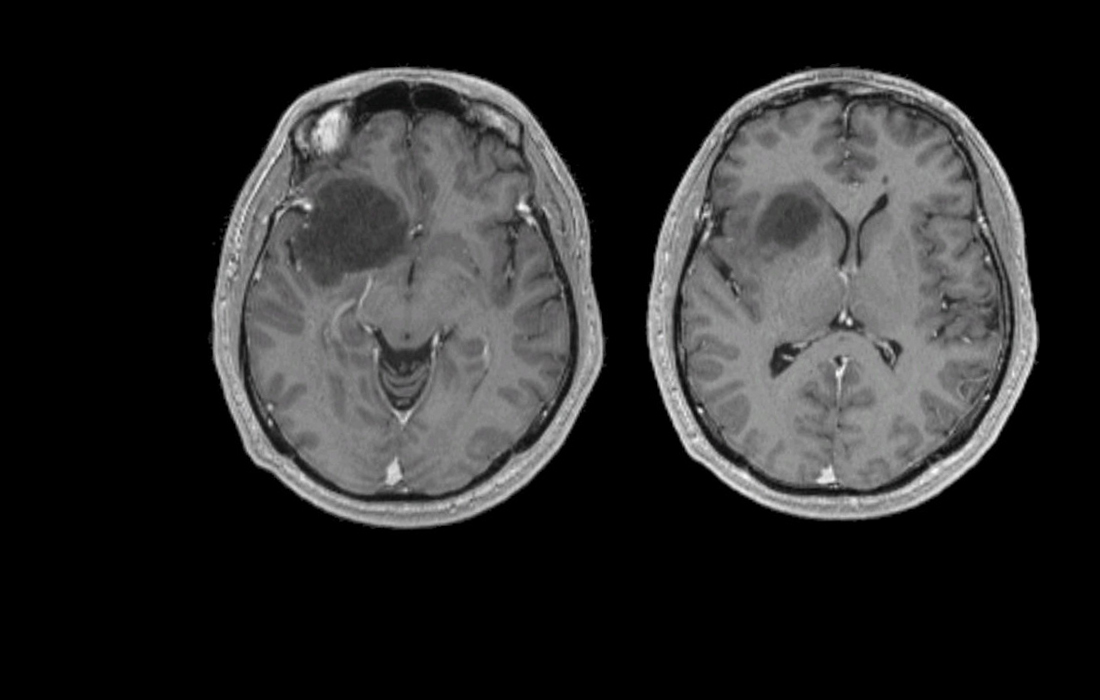
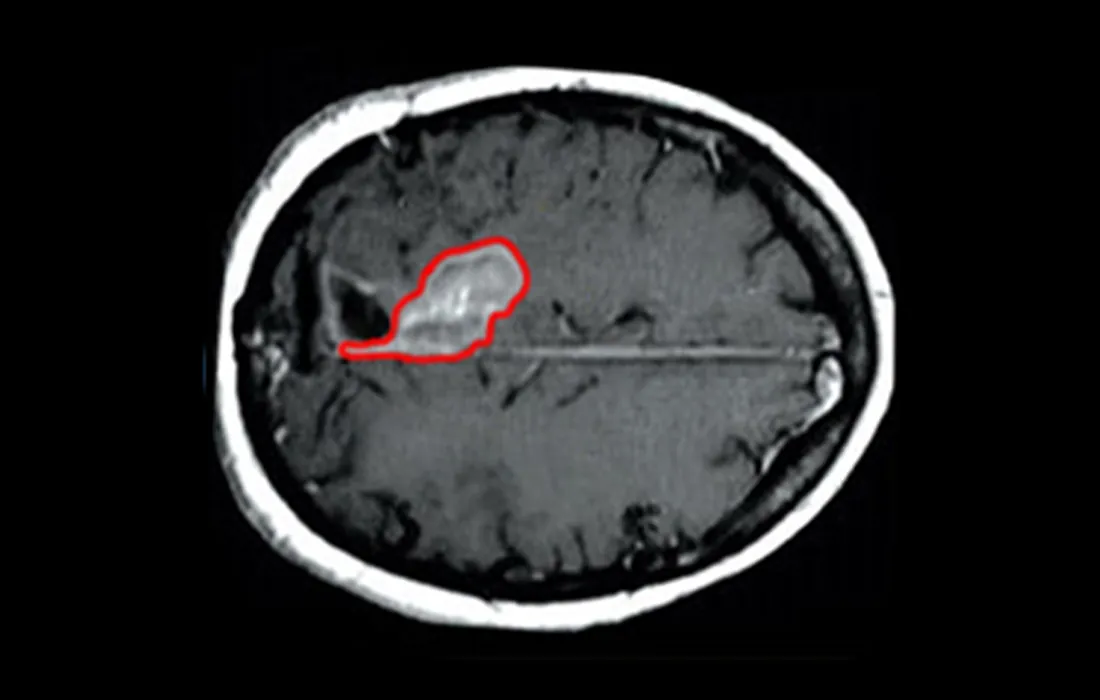
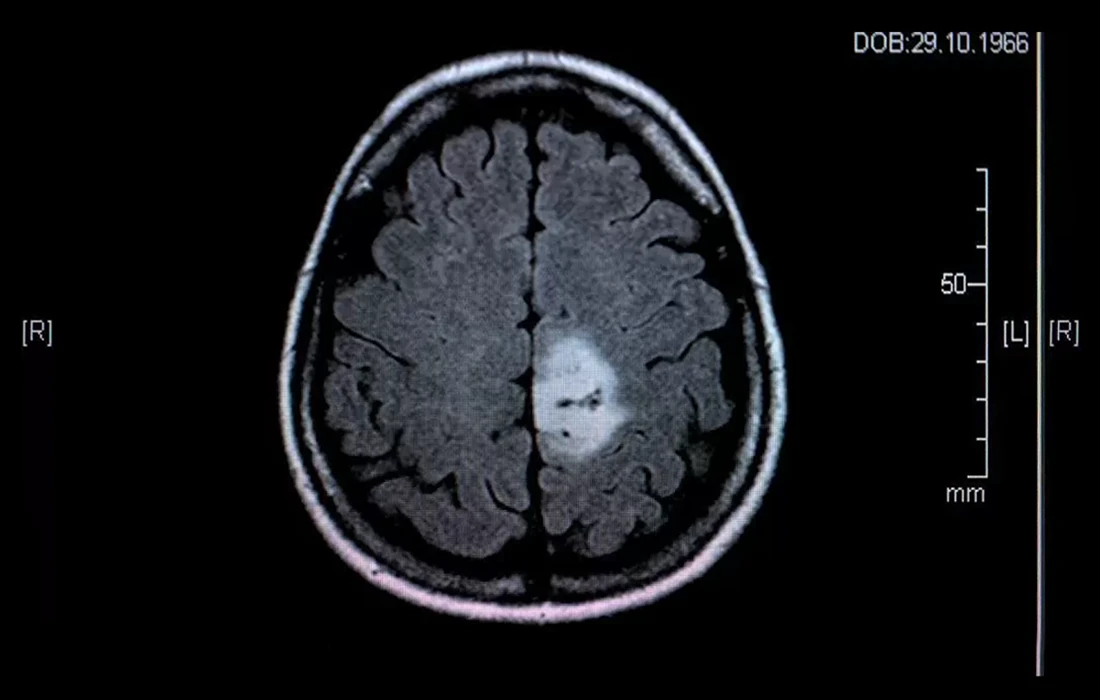
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is the gold standard for glioma detection.
- Contrast-enhanced MRI provides detailed views of tumor margins, swelling, and necrosis.
- Functional MRI (fMRI) maps areas related to movement and speech for safe surgical planning.
- Diffusion and perfusion MRI help characterize tumor cellularity and blood flow.
CT Scan
Used for detecting calcifications and acute bleeding, particularly in emergencies.
Biopsy
A tissue sample is obtained through open surgery or stereotactic needle biopsy to determine the tumor’s pathology. Stereotactic biopsy is especially useful for deep or high-risk tumors.
Molecular Pathology
Testing for biomarkers such as IDH mutation, MGMT promoter methylation, and 1p/19q co-deletion helps determine the prognosis and guide personalized treatment plans.

Treatment Options for Glioma Patients
Glioma treatment is tailored to each patient’s tumor type, grade, age, and overall condition. Treatment options include:
Surgery
The goal is maximum safe resection of the tumor. Techniques include:
- High-magnification microsurgery
- Neuronavigation-assisted procedures
- Intraoperative MRI
- Awake craniotomy for tumors near functional brain regions
Radiotherapy
Postoperative radiation therapy targets remaining tumor cells.
IMRT (Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy) minimizes exposure to healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy
Temozolomide is the standard chemotherapy drug, often administered alongside radiation.
Molecular test results may guide the use of additional or alternative treatments.
Advanced Treatments and Clinical Trials
Eligible patients may benefit from targeted therapies, immunotherapies, or clinical research protocols.
Glioma Treatment in Istanbul: The Collaborative Approach
Specialized centers in Istanbul offer multidisciplinary care in collaboration with academic hospitals. Treatment teams may include neurosurgeons, oncologists, radiologists, and rehabilitation specialists. Comprehensive support is often available for international patients — including interpreter services, accommodation assistance, airport transfers, and post-treatment coordination.
Conclusion
If you’re searching for information like “What is a glioma?”, “Glioblastoma treatment options”, or “Brain tumor surgery in Istanbul,” the key lies in accurate diagnosis and experienced care. With access to advanced imaging, molecular diagnostics, and internationally recognized treatment protocols, Istanbul has become a trusted destination for glioma treatment.
Contact us to learn more or schedule a consultation with a specialist.